Workshop Navigation
Facilitating the Workshop
Purpose: a facilitator’s role is to guide a group toward shared understanding, decision-making, or problem-solving.
Style of Delivery: facilitation is interactive, encouraging active participation, discussion, and group dynamics.
Content: in facilitation, the content often evolves based on group input and collaborative activities.
Tools and Techniques: facilitators use tools like brainstorming exercises, group activities, whiteboards, or even timeboxing techniques to keep participants engaged.
Role of the Audience: in facilitation, the audience plays an active role, engaging in discussions and shaping outcomes.
Outcome: facilitation is more about collaboration, achieve consensus, or making decisions as a group.
Duration
Most WSJF Workshops can be completed in 2-4 hours. If the backlog is very lengthy, or complexity demands, it may require multiple sessions.
Presenting the Process
- Introduction
- What is WSJF?
- Why is prioritization important in Agile?
- The WSJF formula
- Cost of Delay (CoD)
- Job size (duration)
- Formula: WSJF = CoD/Job size
- Application
- Identifying high-value features or tasks
- Balancing effort against payoff across projects
- Benefits
- Faster delivery of high-impact work
- Improved alignment on business goals
- Example Scenarios
- Use real-world or hypothetical examples to illustrate WSJF in action
- Implementation Tips
- Tools or frameworks (like SAFe boards)
- Common challenges and how to overcome them
- Q & A or Interactive Exercise
- Let your audience practice using the WSJF formula
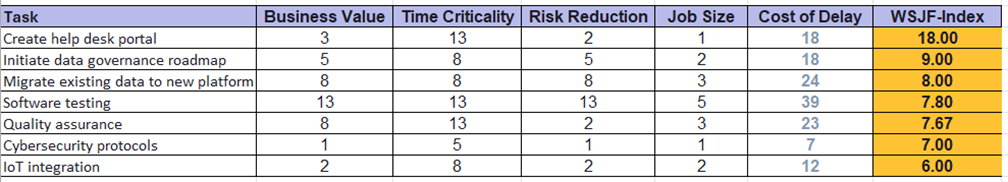
Example Board
Common Anti-Patterns
- Ignoring relative estimation: using absolute values for cost of delay instead of relative estimation can spew prioritization and make comparisons difficult.
- Overemphasis on one factor: focusing too much on one element of cost of delay while neglecting others like time criticality or risk reduction.
- Static prioritization: not updating WSJF scores regularly based on changing circumstances and new information can lead to outdated priorities.
- Misinterpreting job duration: misestimating job duration either by over or underestimating can result in incorrect WSJF scores and poor prioritization.
- Ignoring sunk costs: calculating in sunk costs when calculating WSJF, which goes against Lean principles and can lead to inefficient prioritization.
- Lack of collaboration: not involving the entire team in the WSJF process can lead to biased prioritization and lack of buy-in from team members.
- Complexity over simplicity: making the WSJF calculation overly complex which can deter teams from using it effectively.
